Understanding and Treating 4 Common Types of Heart Disease
- By Admin
- •
- 26 Jul, 2019
- •

Without a fully functional heart, blood, oxygen, and nutrients will not be circulated through the body, increasing your risk of a variety of life-threatening conditions. Various types of heart disease, for example, could result in a heart attack and even death. As a matter of fact, an estimated 610,000 people in the United States die every year because of heart disease.
Some people are surprised to learn that heart disease comes in many forms. Because they all can be deadly, proper understanding is imperative. With this guide and your heart specialist's help, you will become better able to prevent a few common forms of heart disease.
1. Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is a common, yet potentially dangerous, form of heart disease. Also known as atherosclerosis, this disease is basically a hardening or clogging of the arteries from cholesterol/fat deposits known as plaque.
If the arteries are clogged with hardened cholesterol and plaque, blood will not be able to flow through the circulatory system properly. This essentially starves the heart and body of oxygen and nutrients that are necessary for life.
A primary sign of heart disease is angina, a form of chest pain. Heart attacks, both minor and more severe, are common in patients who have coronary artery disease.
Patients who have coronary artery disease have many treatment options. For example, balloon angioplasty can be an effective option for removing hardened cholesterol and plaque from the arteries to improve blood flow.
2. Congenital Heart Disease
If you were born with one or more abnormalities of the heart, you will be diagnosed with congenital heart disease. The type of defect affecting the heart may range from minor, which may or may not cause symptoms, or more severe, which will show symptoms and become life-threatening without proper management.
A few common symptoms of congenital heart disease are:
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue that occurs quickly after exertion
- Edema, or swelling of tissue/organs
- Cyanosis, or bluish tint to skin/lips/fingertips
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you should have your heart and heart functions tested immediately. Once the actual defect is determined, doctors will design a treatment plan suited to your specific needs.
3. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
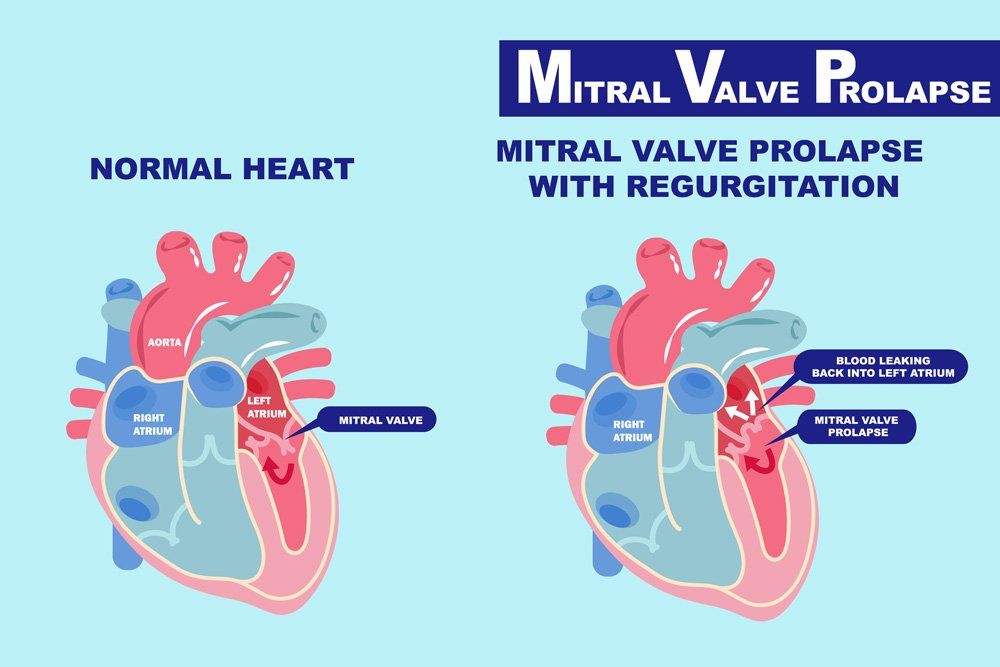
Another common form of heart disease is dilated cardiomyopathy. This condition occurs when the left ventricle, which is the heart's main pumping chamber, is weakened or enlarged. This distress of the left ventricle prevents the heart from pumping blood effectively and efficiently, which could lead to a heart attack or heart failure.
Symptoms are not always present or noticeable in patients who have dilated cardiomyopathy. However, if you are experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, weight gain, swelling of the lower extremities, dizziness, fainting, and/or heart palpitations, your heart specialist may want to test for dilated cardiomyopathy.
Various medications to manage symptoms and decrease the risk of heart failure will be prescribed if you are diagnosed with dilated cardiomyopathy.
If you have a more severe case of the disease, surgery may be recommended. Surgery may involve placing a pacemaker to stimulate both ventricles to improve the overall function of the heart.
Other surgical options include shocking the heart's muscles using a defibrillator to help maintain normal rhythms. Surgical repair of the left ventricle may also be an option recommended.
4. Arrhythmia
Lastly, an arrhythmia is a common type of heart disease. Even though this irregular heartbeat or fluttering rhythm is usually harmless, doctors should still monitor your arrhythmia. In addition, if the arrhythmia is severe or it is caused by another underlying heart condition, treatment may be necessary.
Pacemakers are often used to control abnormal heart rhythms, but less-invasive options are also available if you have a less severe type of arrhythmia. Medications, electrical shock, and vagal maneuvers that stop some forms of arrhythmia can all be beneficial.
Understanding different versions of heart disease is important for your health and wellness. For more information on these or other types of heart disease/conditions, contact Anderson Heart PC.